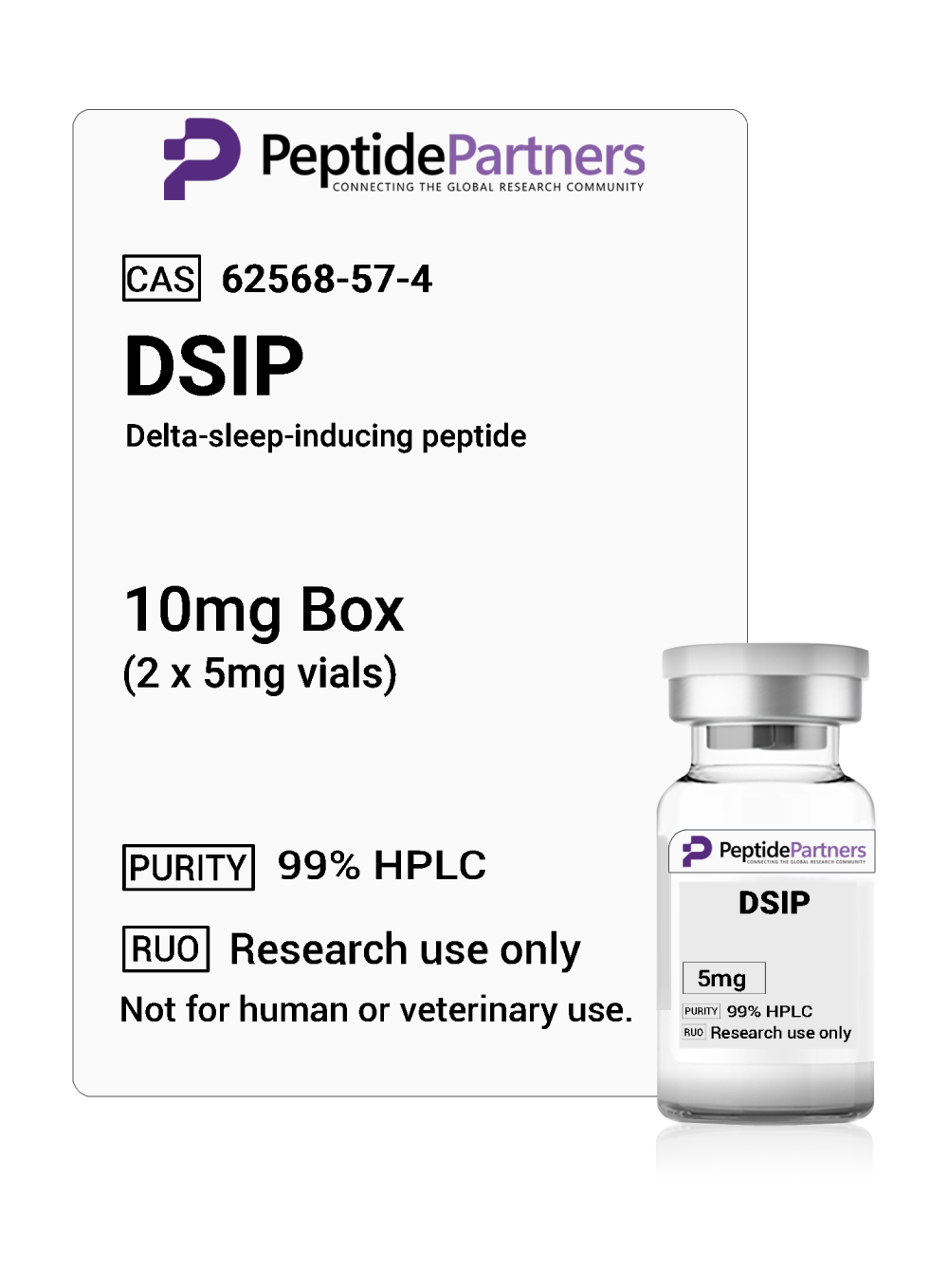
DSIP (10mg – 50mg)
Price range: $69.00 through $275.00
Description
DSIP
Delta-sleep-inducing peptide
Save over 40%!
Swipe right to view full table →
 |
Peptide Sciences | Core Peptides | |
Cost per milligram |
$5.5 – $6.9 |
$10.00 | $8.20 |
Purity |
99.88% |
98.7% | 98.5% |
Certified Endotoxin-safe |
Yes |
No | No |
Independently Tested |
Yes |
No | No |
Peptide Partners Manufacturer Id: SH07
Batch Id: DS20250820
Overview
(For educational purposes only)
Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide (DSIP) is a naturally occurring neuropeptide that has been investigated for its role in the regulation of sleep, stress response, and neuroendocrine modulation. Discovered in the 1970s, DSIP continues to attract research interest due to its influence on delta-wave sleep, potential stress-protective effects, and unexplained distribution and biosynthesis.
Molecular Identity and Structure
CAS Number: 62568-57-4
Amino Acid Sequence: Trp-Ala-Gly-Gly-Asp-Ala-Ser-Gly-Glu (WAGGDASGE)
Molecular Formula: C35H48N10O15
Molecular Weight: 848.8–849.0 g/mol
PubChem CID: 68816
Discovery Year: 1974 (by G. Schoeneberger and M. Monnier)[1][2]
Broad Category: Endogenous neuropeptide; sleep-promoting/regulatory peptide[3][1]
Biochemistry and Distribution
DSIP is an amphiphilic nonapeptide that occurs in both free and bound forms throughout the hypothalamus, limbic system, pituitary gland, and various peripheral organs (including the gut and pancreas). In the pituitary, it colocalizes with several peptide and non-peptide hormones, such as ACTH, MSH, and TSH. Notably, DSIP is commonly detected in plasma and secretory cells of the gastrointestinal tract, often co-localized with glucagon.[4][1][3]
Biological Functions
DSIP’s primary function is linked to the promotion of delta-wave (SWS, “deep” non-REM) sleep in mammals, as indicated by its name and classical pharmacological experiments. Research has shown that DSIP can modulate sleep patterns, regulate circadian rhythms, influence hormone levels (notably reducing corticotropin, increasing growth hormone, and other stress axis hormones), and affect neuronal transmitter activity. The peptide also demonstrates stress-protective, anti-seizure, and immunomodulatory effects in various animal models.[2][1]
DSIP’s action in the brain seems to be associated with NMDA receptor activity, and it may interact with the MAPK cascade, and is possibly homologous to the glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper protein GILZ, implicating it in stress physiology.[1]
Stability and Metabolism
DSIP is characterized by low molecular stability in vitro, exhibiting a half-life of about 15 minutes due to rapid enzymatic degradation. It is hypothesized that in vivo, DSIP is stabilized by carrier proteins or is stored as a component of a larger precursor molecule, though the gene coding for its precursor has not yet been conclusively identified in mammals.[4][1]
Potential Clinical Roles and Research
DSIP’s sleep, anti-stress, and neuroendocrine effects have prompted exploration of its therapeutic potential in sleep disorders, pain syndromes, epilepsy, and some neuroendocrine and stress-related illnesses. However, efficacy and mechanisms in human clinical trials remain insufficiently defined, and DSIP is primarily considered an experimental neuropeptide at present.[5][3]
Conclusion
Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide is a unique, endogenous neuropeptide notable for its sleep-promoting and neuroendocrine effects. Despite some gaps in understanding regarding its synthesis and signaling pathways, DSIP remains of strong research interest for roles in sleep regulation, stress physiology, and neuroendocrine modulation. Clinical application is experimental and awaits more definitive research to elucidate its mechanisms, therapeutic value, and long-term safety profile.[3][2][5][1][4]
⁂
-
https://www.biosyn.com/tew/deltasleep-inducing-peptide-or-dsip.aspx
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/delta-sleep-inducing-peptide
-
https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB6478191.htm
-
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03693.x
Additional information
| Quantity (mg) | 10mg, 25mg, 50mg |
|---|


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.